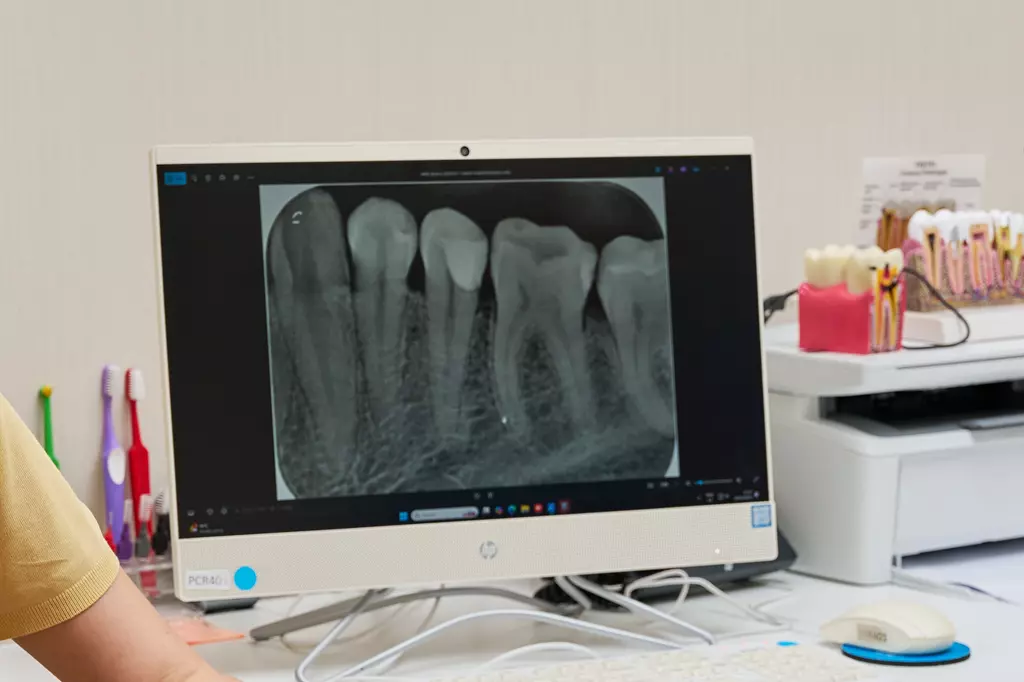
Types of Dental X-rays
Bitewing X-rays
Used to detect cavities between teeth and assess bone levels affected by gum disease.
Periapical X-rays
Capture a full view of a single tooth from crown to root, helping identify inflammation, cysts, or root-related changes.
Panoramic X-ray (OPG)
Provides a complete overview of the mouth, including both jaws, teeth, joints, and sinuses.
Cephalometric X-rays
Used primarily in orthodontics to evaluate jaw position, growth patterns, and bite alignment.
Cone Beam CT (CBCT)
A 3D scan used for implant planning, complex diagnostics, bone assessment, and detection of hidden dental issues.
Benefits of Dental X-rays
You may need imaging when you:
- Attend a routine examination
- Have tooth or gum pain
- Prepare for braces, implants, or extractions
- Monitor the success of previous treatment
- Experience dental trauma
Safety of Digital Dental X-rays
Digital systems significantly reduce radiation exposure. Protective aprons ensure additional safety. If you are pregnant, inform your dentist in advance so we can take the safest diagnostic approach.
Conclusion
Dental X-rays remain essential for timely diagnosis and accurate treatment planning. If you have not updated your imaging recently, discuss it at your next appointment in Abu Dhabi.