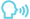Why Gum Issues Are Easy to Miss and Dangerous to Ignore
Periodontal disease is known as a “silent condition” for a reason. Many people assume that gum problems will be painful or obvious, but they often start with subtle symptoms:
- Occasional bleeding during brushing
- Gums that appear red or slightly puffy
- Bad breath that lingers
- Sensitivity at the gumline
- Gradual spaces forming between teeth
These are not always dramatic and often overlooked problems. But beneath the surface, chronic inflammation may already be weakening the structures that support your teeth. In our practice on Al Reem Island, we catch and treat these issues early so they never get the chance to escalate.
What Is Periodontal Therapy?
Periodontal therapy includes a wide range of procedures used to treat gum infections, stop bone loss, and regenerate healthy tissues. The right treatment depends on your current stage of disease and your long-term goals.
Common options include:
- Deep cleaning (also known as scaling and root planing) to remove bacteria from beneath the gums
- Laser therapy to sterilise inflamed pockets with precision
- Tissue grafts to rebuild lost gum structure
- Bone regeneration in areas where periodontal infection has caused loss
- Occlusal adjustment to reduce bite pressure on compromised teeth
Our focus is always on preserving your natural teeth for as long as possible while reducing the risks.
Scaling and Root Planing: Deep Cleaning with a Purpose
This is not the kind of cleaning you get during a regular check-up. When plaque hardens below the gumline and starts irritating the tissues around your teeth, it has to be removed professionally.
At TRUE SMILE, our deep cleaning method uses both ultrasonic instruments and manual tools to ensure thorough, gentle removal of harmful deposits. Afterward, we smooth the root surfaces so bacteria are less likely to reattach.
We often combine deep cleaning with antibacterial agents that are applied directly into the affected areas. This speeds healing and reduces inflammation. If you have been searching for deep cleaning for gums in Abu Dhabi that is thorough but not painful, this is it.
Gum Surgery: When Non-Surgical Options Are Not Enough
In moderate to severe periodontitis, deep cleaning alone may not be sufficient. In those cases, we consider surgical options designed to eliminate infection and reconstruct damaged tissue.
Flap Surgery
This procedure allows us to gently open the gums to reach deep pockets of infection. Once cleaned, the tissue is repositioned to reduce future plaque accumulation and help the gums heal in a more secure position.
Gum Grafting
If your gums have receded, leaving the roots exposed, we can rebuild lost tissue using biocompatible grafts or your own tissue. This helps reduce sensitivity, improve appearance, and prevent further loss.
Bone Grafting
Periodontal disease often leads to bone deterioration. Using grafting materials, we can stimulate bone regeneration around your teeth or in preparation for dental implants.
Guided Tissue Regeneration
We place a membrane between bone and soft tissue to direct healing in a way that favours regrowth of both structures.
Patients looking for gum grafting or flap surgery for periodontitis in Abu Dhabi trust our clinic for its modern techniques and compassionate care. We perform these procedures with precision and only when absolutely necessary.
Laser Periodontics: Healing with Light
One of the most innovative tools in periodontal care is the dental laser. This device allows us to target and remove infected gum tissue while leaving healthy tissue intact. It also helps kill bacteria deep in periodontal pockets and encourages natural healing.
Laser gum treatment in Abu Dhabi is becoming more popular because it often means:
- Less bleeding during the procedure
- Faster recovery times
- Reduced need for sutures or cutting
- Less discomfort afterward
We offer laser options as either standalone treatments or as enhancements to conventional procedures. They are especially helpful for patients who prefer less invasive methods.
Maintenance Matters: Keeping Results Long-Term
Once your gums are stable, the next phase is keeping them healthy. Periodontal maintenance is a long-term plan for protecting your results and preventing new disease.
This typically includes:
- Specialised cleanings every three to four months
- Monitoring for changes in gum pocket depth
- Reassessment of risk factors
- Homecare guidance that adapts to your lifestyle
If you have had previous gum therapy, your mouth needs more frequent follow-ups than someone with no history of disease. We personalise your recall schedule and work closely with you to ensure that inflammation does not return.
When to See a Periodontist
You do not need to be in pain to seek expert care. In fact, some of our most successful cases began with patients who simply had a few questions. You may want to schedule an exam if you:
- Have gums that bleed easily or feel tender
- Notice changes in how your teeth fit together
- Are planning for orthodontic work or dental implants
- Manage diabetes or cardiovascular conditions
- Are pregnant and concerned about oral inflammation
- Have been told by your general dentist that you have “pockets” or early gum disease
We are also known as a trusted expat dental clinic for periodontics in Abu Dhabi. Whether you are here temporarily or long-term, our care is built for international patients who want clarity, consistency, and communication.
What Happens During a Visit?
We want you to feel informed, comfortable, and never rushed. A typical visit includes:
- A detailed exam, including 3D imaging and gum probing
- A full diagnosis and explanation of your current gum health
- A treatment plan that is staged and easy to understand
- Local anaesthesia or sedation if needed for comfort
- Follow-up instructions and homecare coaching
- Transparent pricing, with help understanding your insurance coverage
We also understand that timing matters. For those with tight schedules, we offer evening and weekend appointments.
Why Patients Trust TRUE SMILE
Located on Al Reem Island, TRUE SMILE Dental Center is easily accessible for families and working professionals across Abu Dhabi. Our multilingual team brings together international clinical training with a patient-first approach, ensuring that every visit feels welcoming and understood. We offer same-day appointment requests via WhatsApp for urgent concerns, and provide nitrous oxide sedation when needed to help anxious patients feel calm and relaxed during treatment.
Consultations are pressure-free, with clear, honest communication at every step. As a recognised provider of advanced gum disease treatment in Abu Dhabi, we take the time to explain your condition, offer conservative options whenever possible, and support you throughout your journey from first diagnosis to long-term maintenance.